Methodology for the creation of the Maritime Boundaries
Data collection and boundaries calculations
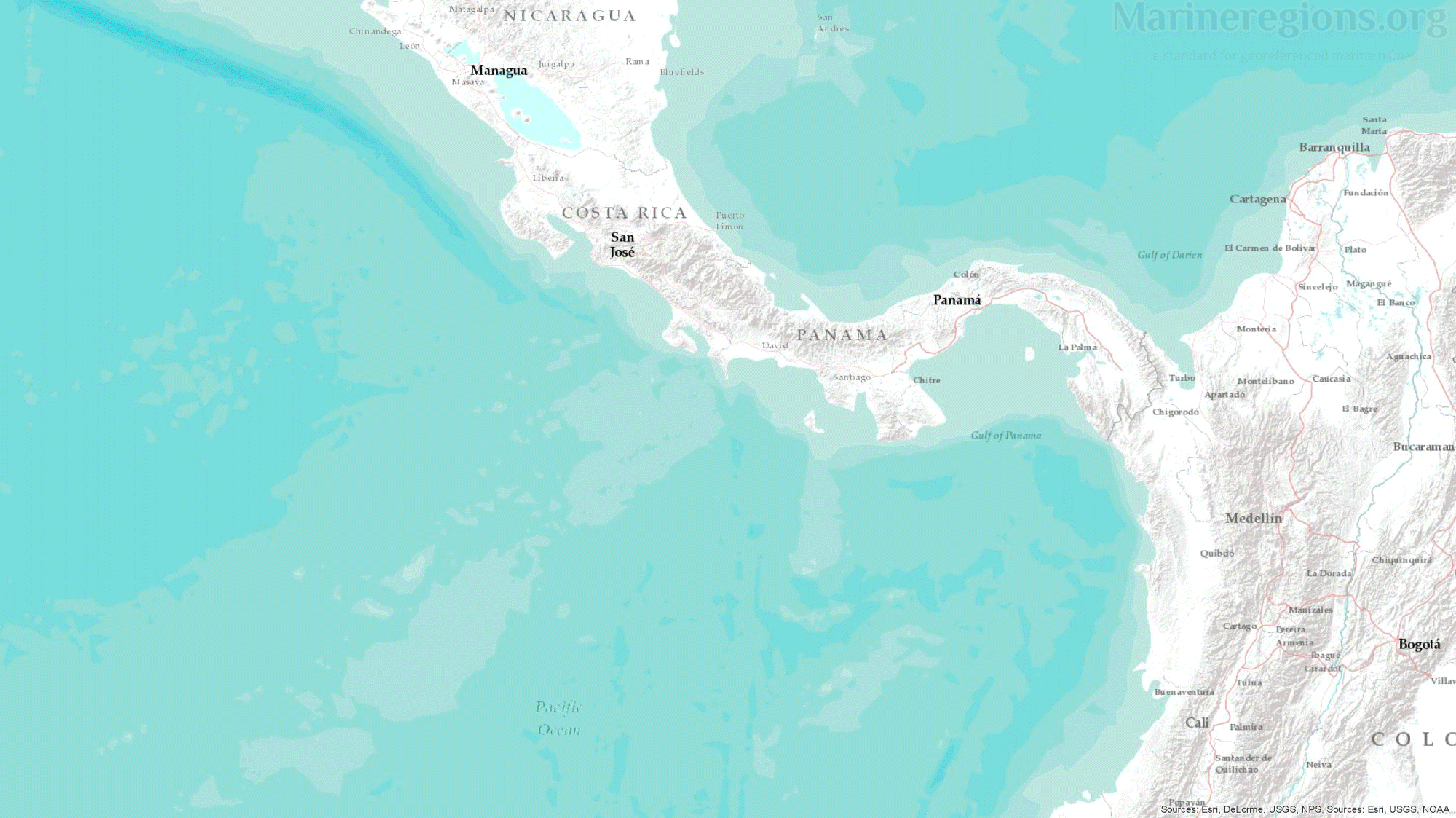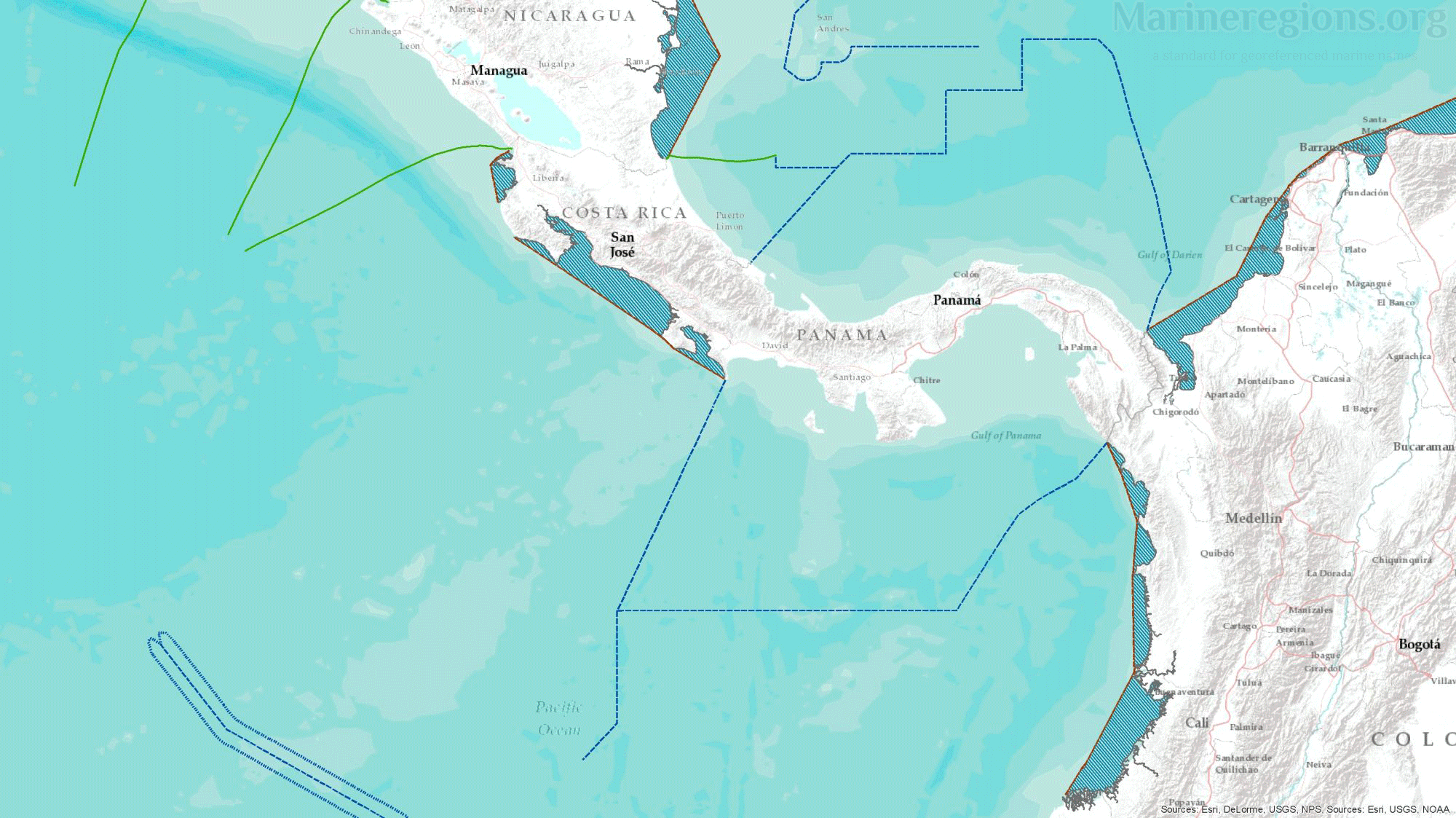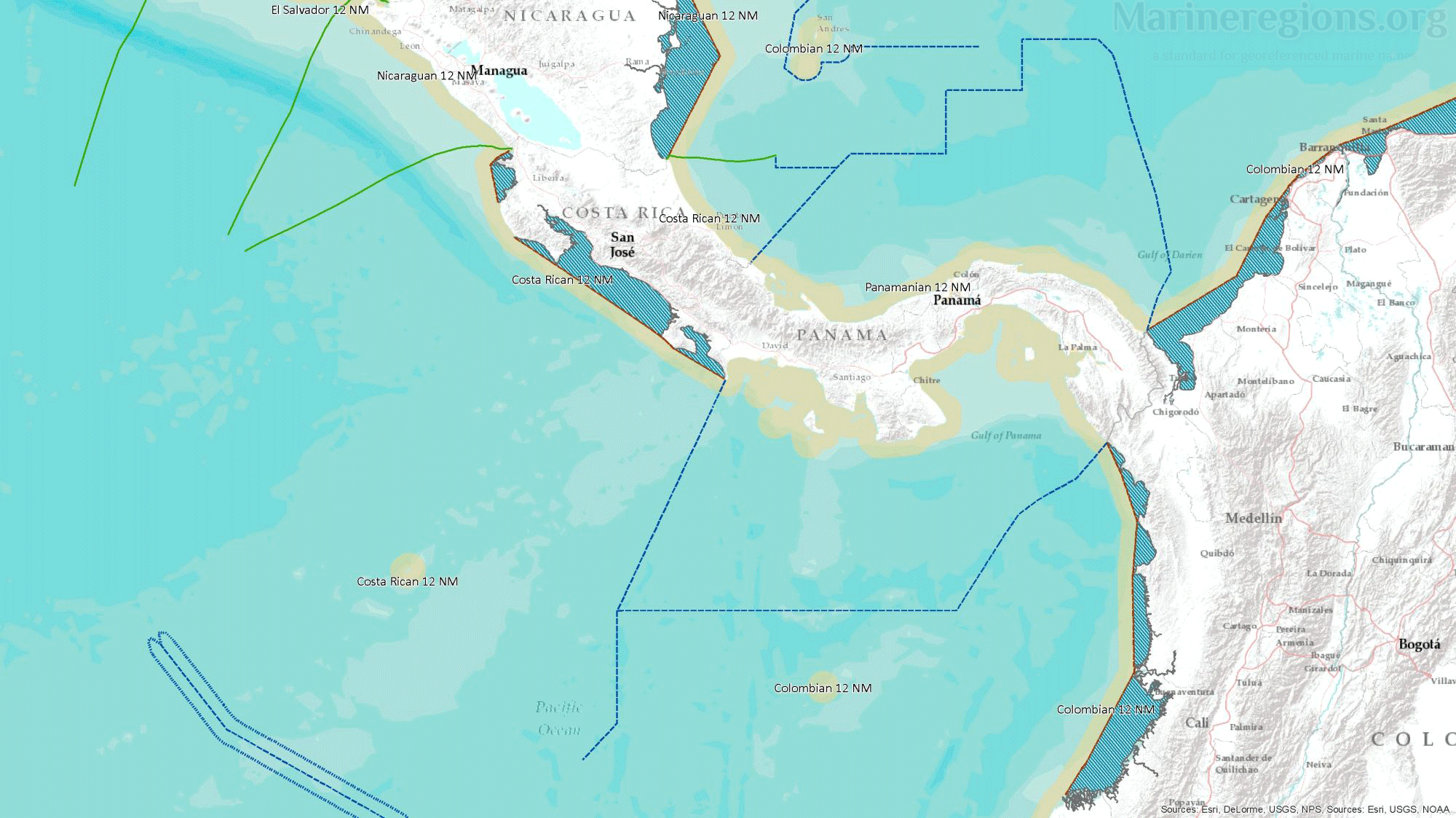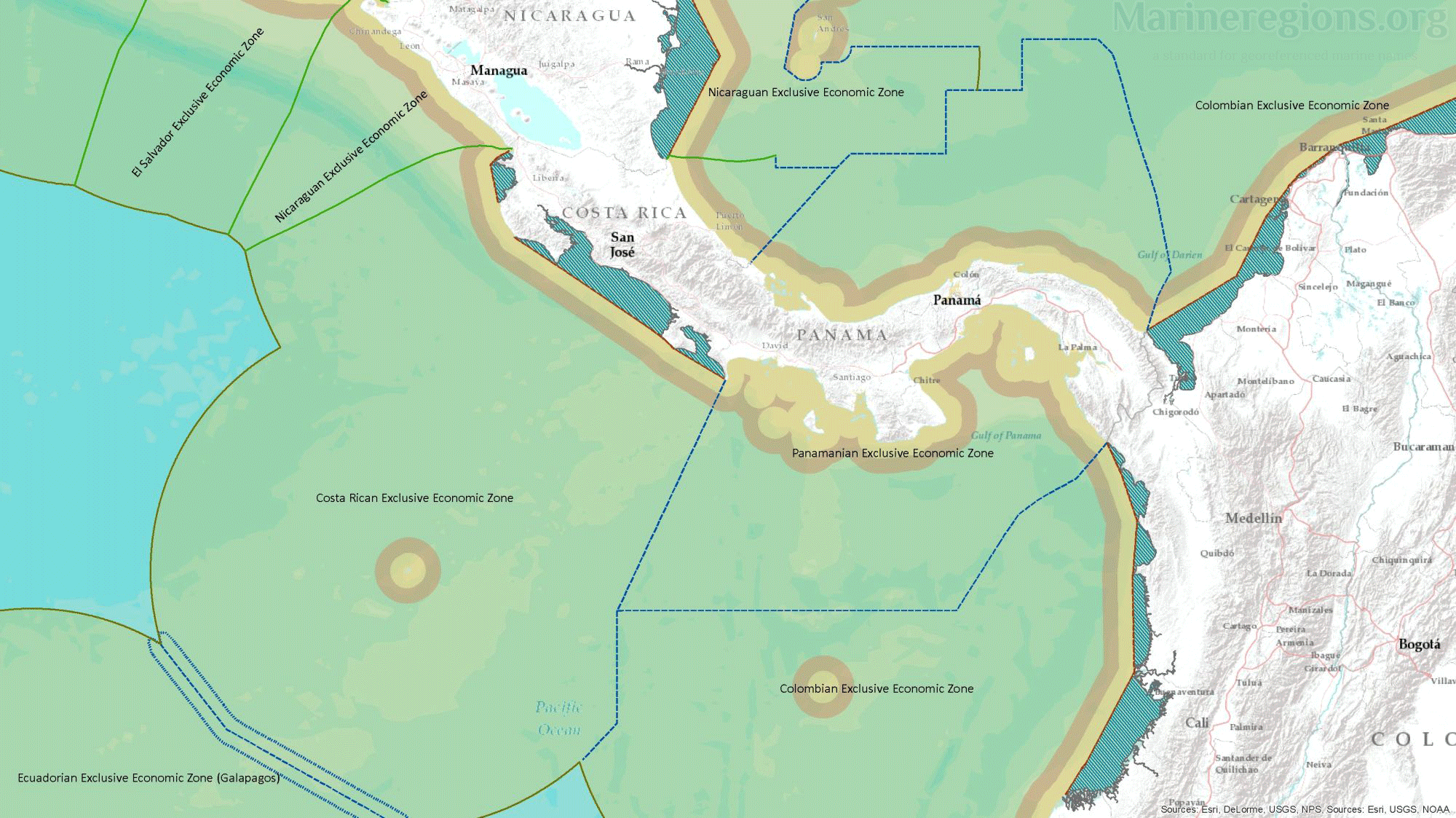
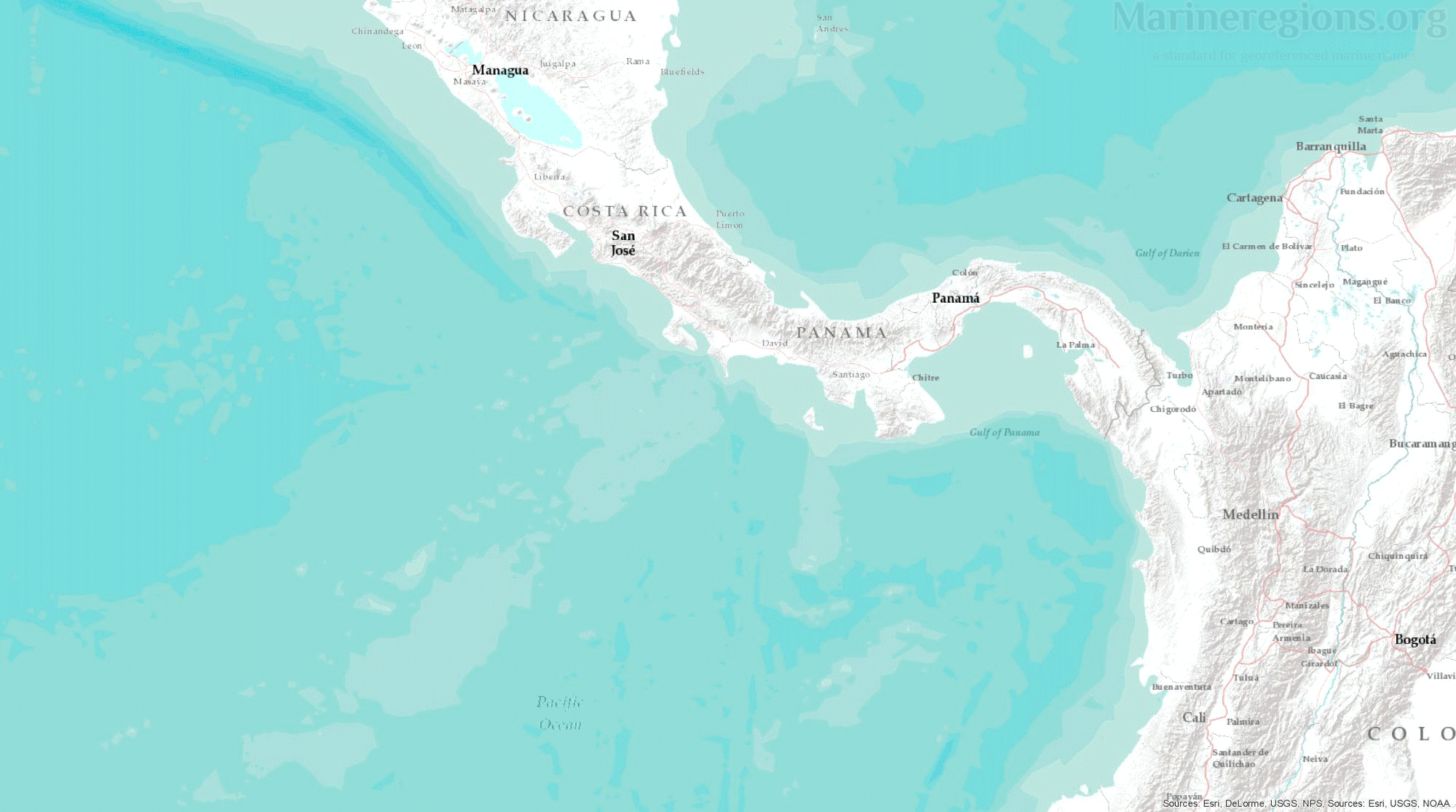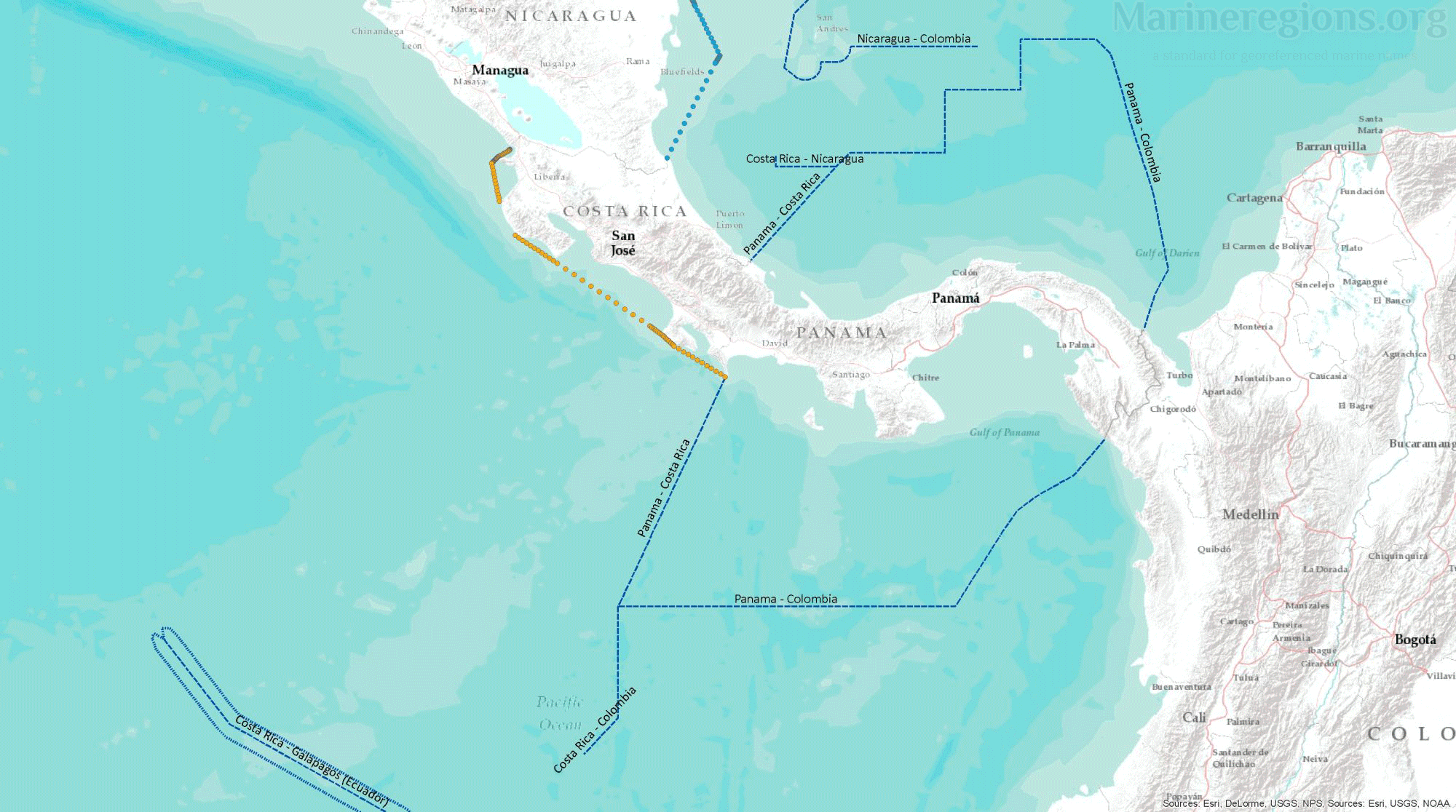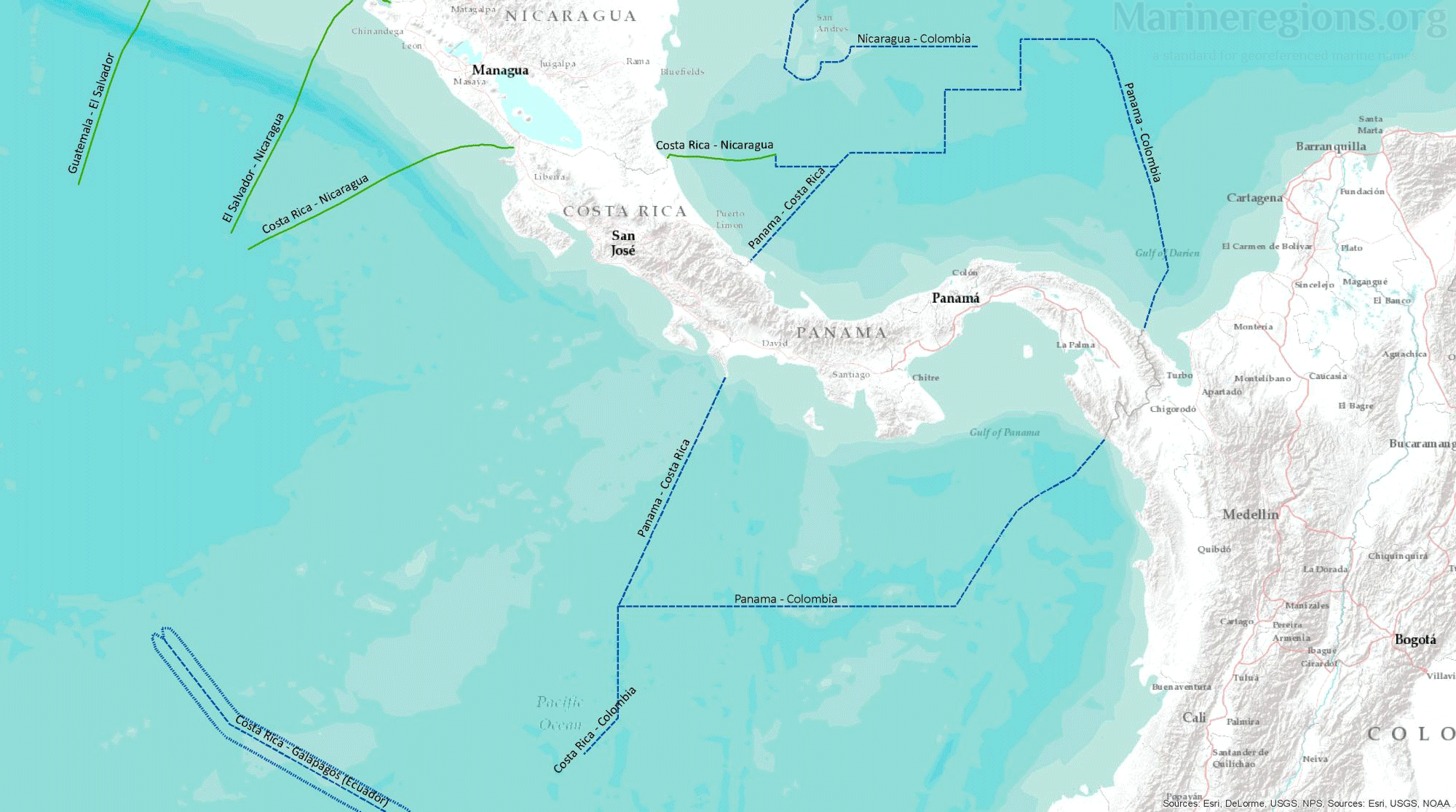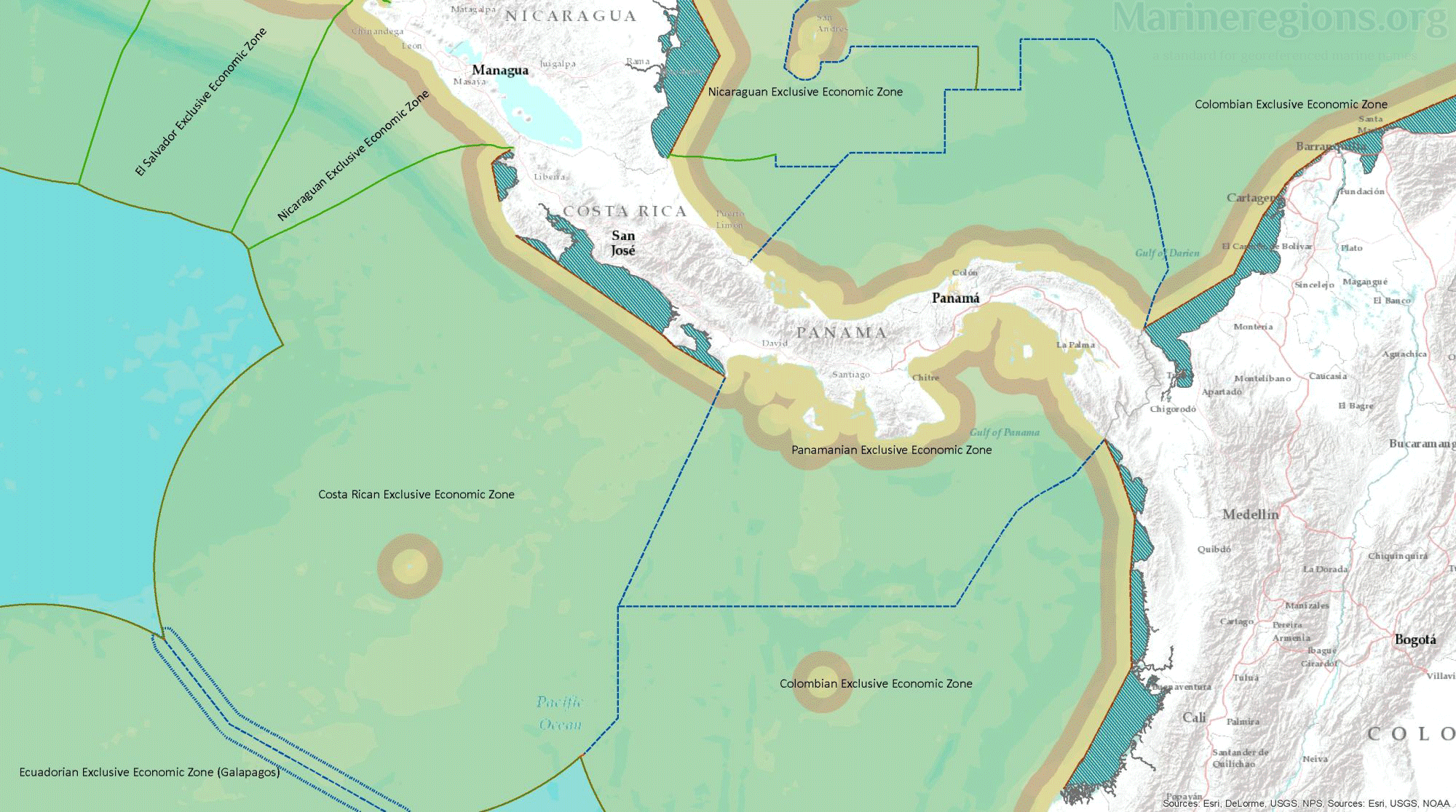
The Maritime Boundaries version 12 are now available on the Marine Regions website. This version builds further on what was made in earlier versions, includes new treaties and corrected inconsistensies. In this new release, Marine Regions makes available all areas included in the provisions of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). These areas are Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ), Territorial Seas (TS), Contiguous Zones (CZ), Internal Waters (IW), and Archipelagic Waters (AW). The High Seas (HS) and Extended Continental Shelves (ECS) are also available, but are based on version 11 of the Maritime Boundaries dataset. Please note that for the delineation of our EEZ, we include the archipelagic waters, internal waters and territorial seas of each country. This is a deviation from the UNCLOS EEZ definition.
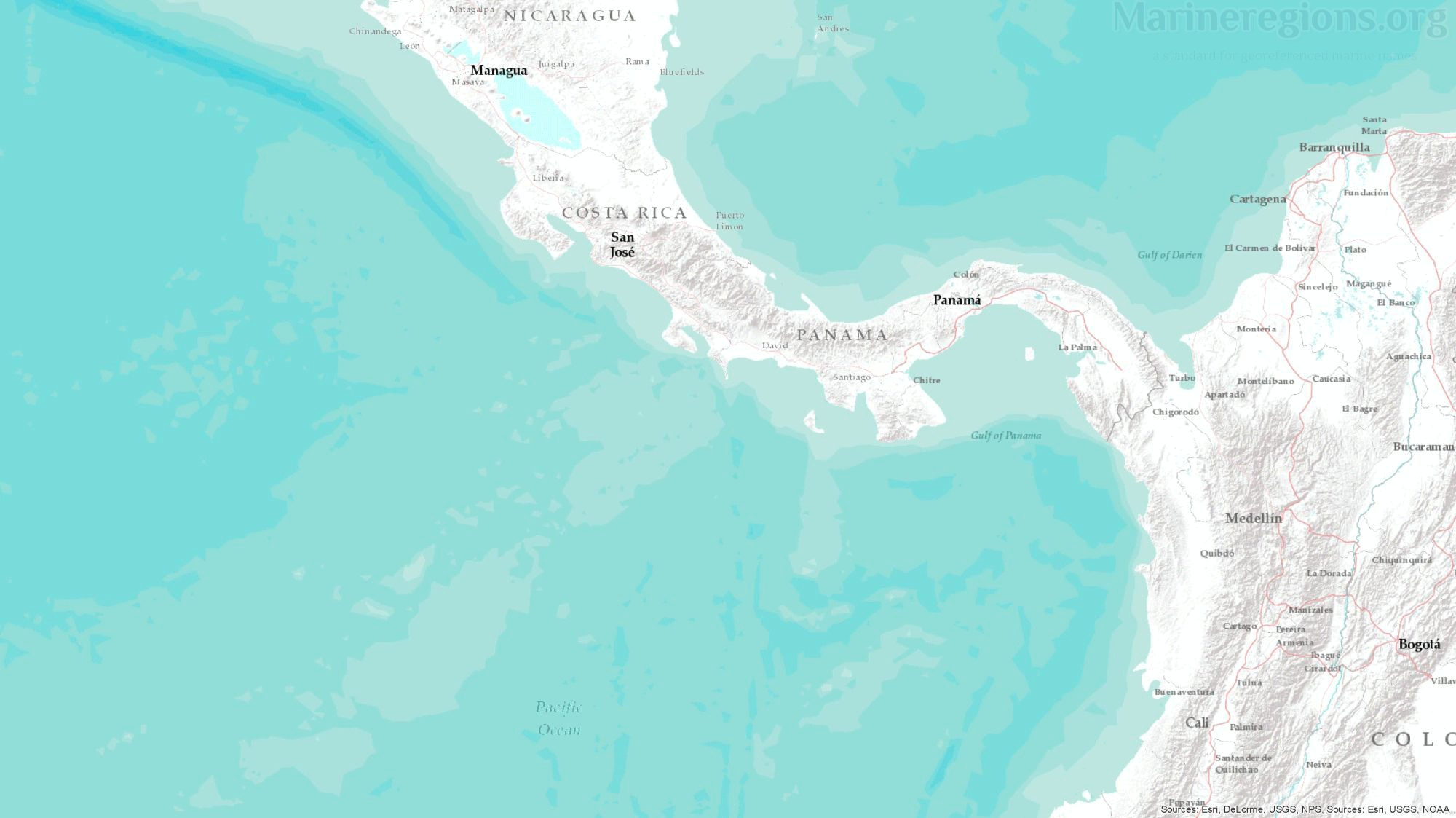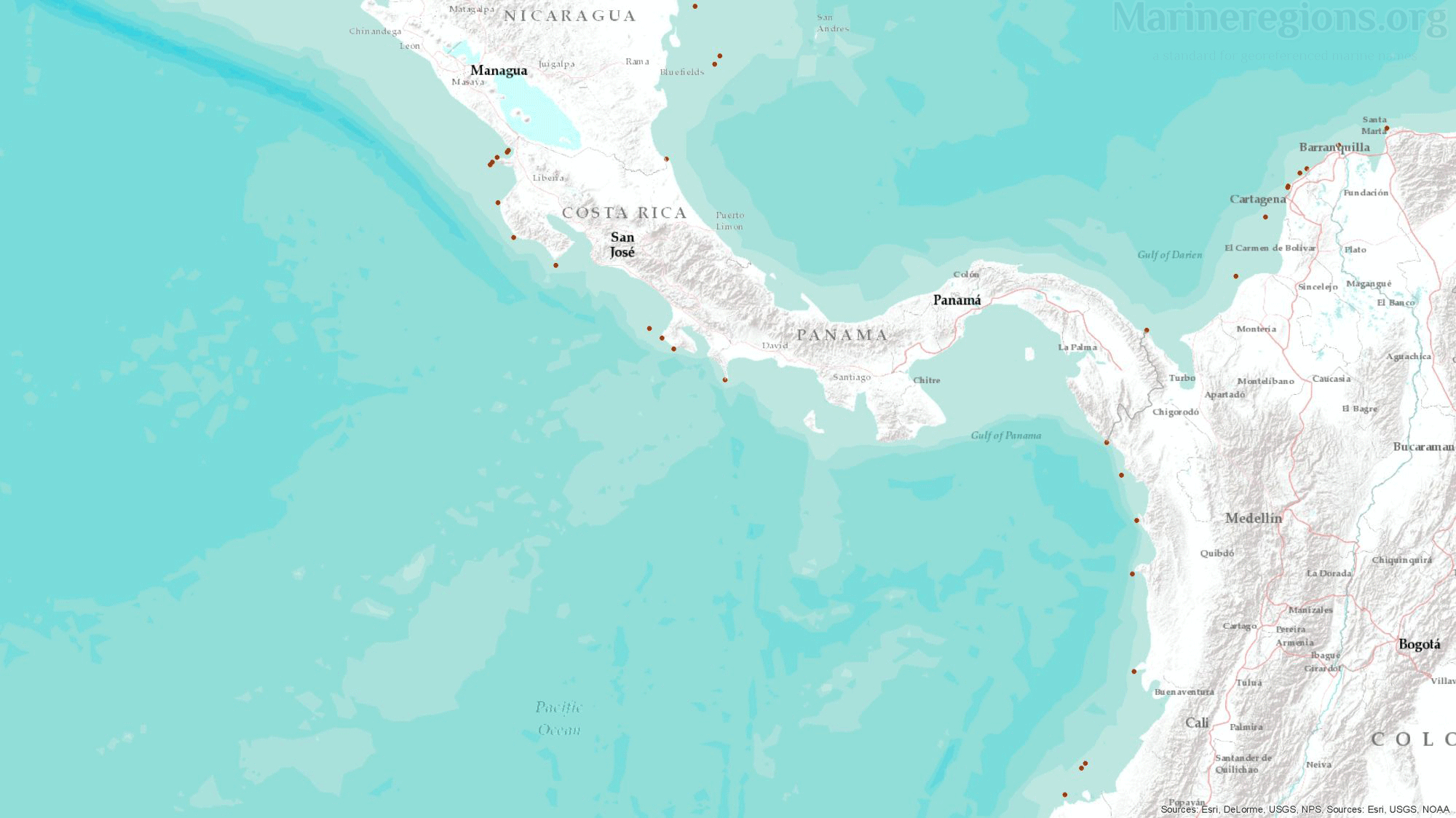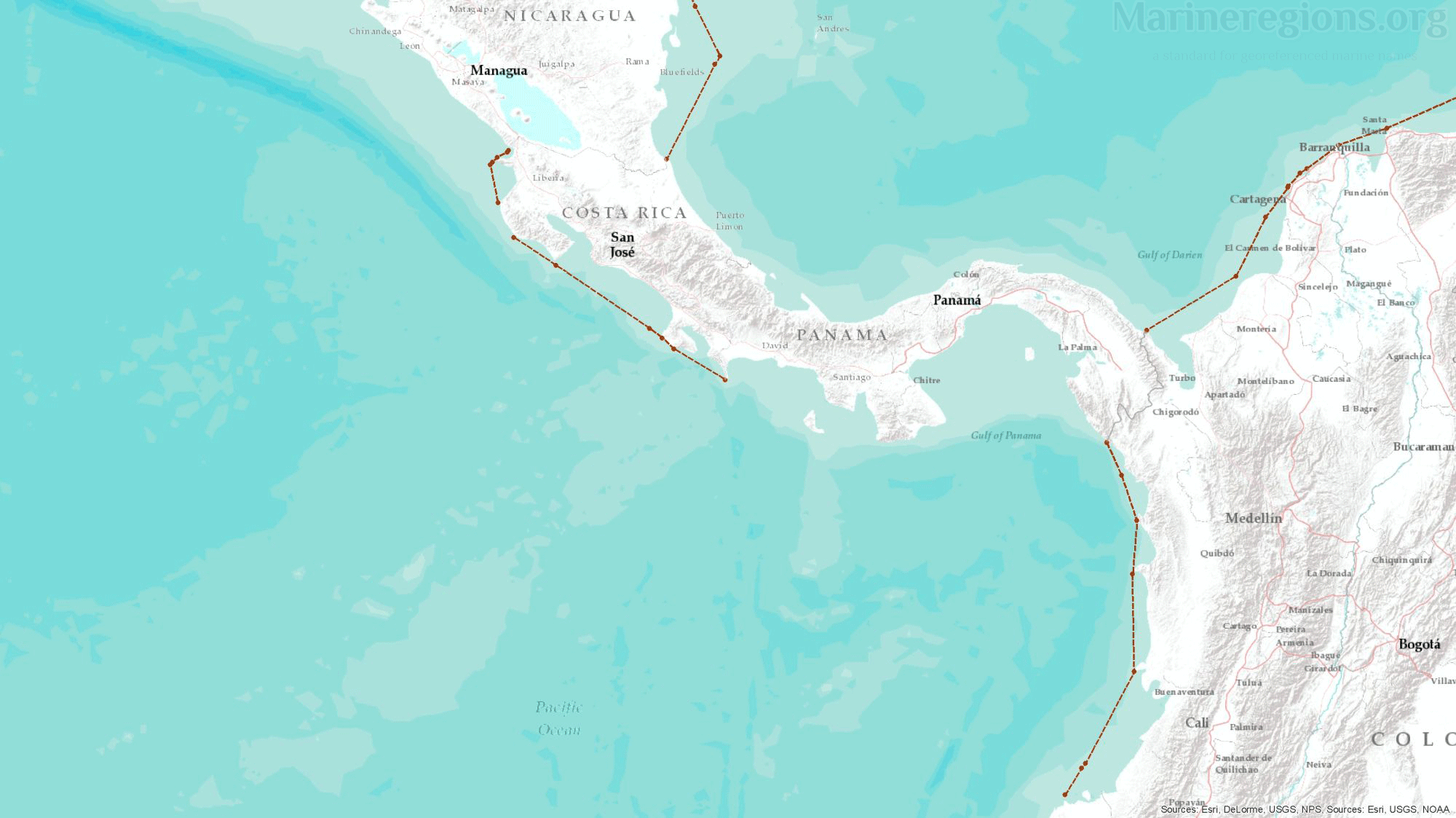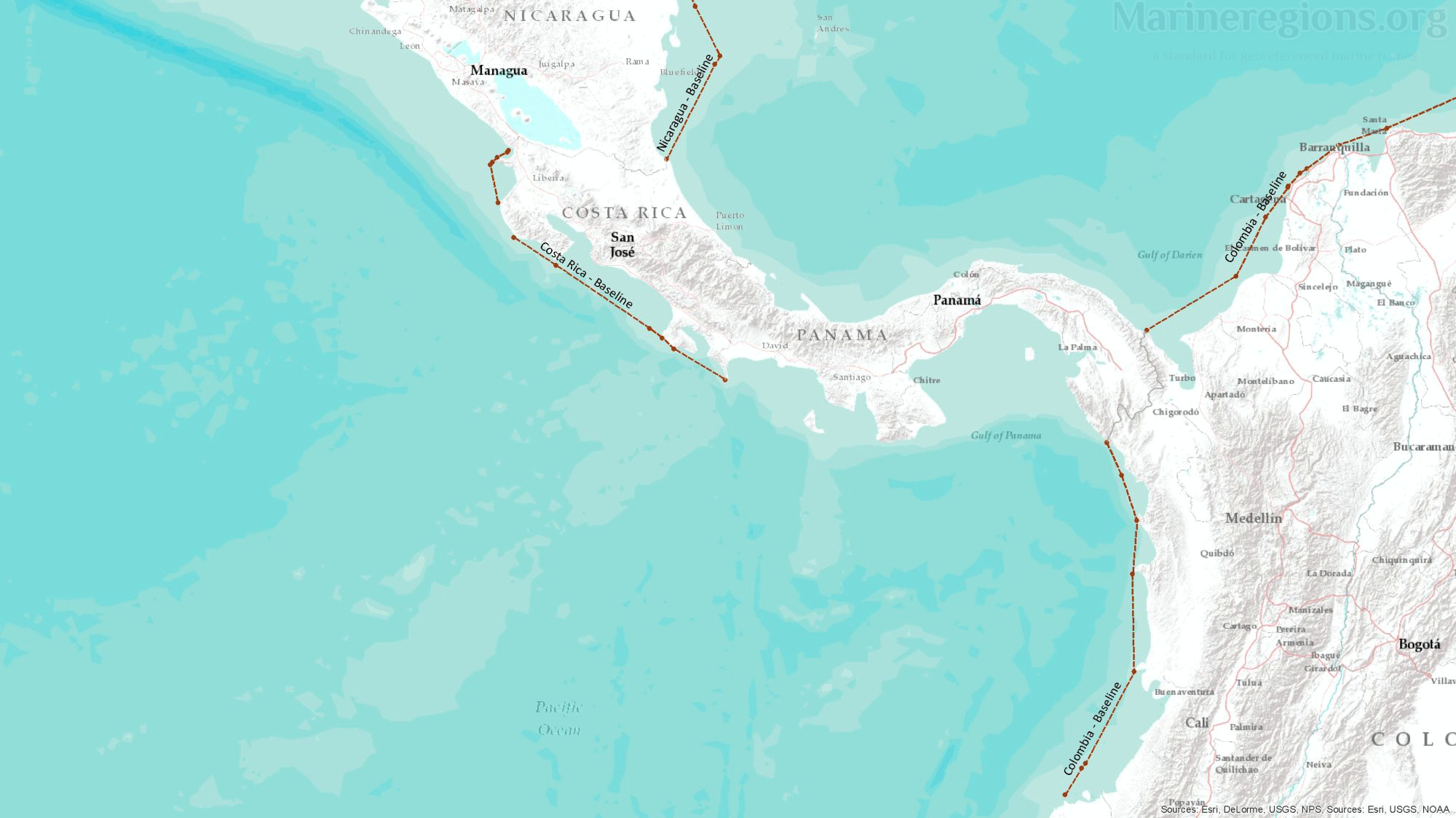
Baselines
The maritime boundaries and areas are calculated from the baselines. In the Maritime Boundaries dataset, the baselines used were a combination of a coastline as a proxy for the low-water line (the normal baseline described in UNCLOS) and straight or archipelagic baselines. The source for the straight baselines was primarily the United Nations repository of all the claims from UNCLOS’s signatories: DOALOS. In addition to this main source, others were also used to complete the straight baselines database such as national legislation on maritime delimitations, agreements, treaties, USA Department of State, among others.
The ESRI Countries 2014 was the primary source for the Maritime Boundaries v12 baseline. The coastline was extracted from the ESRI Countries 2014 and then combined with reefs data extracted from Coral Reef Distribution UNEP for the countries where reefs were fundamental for the correct calculation of the maritime areas, as intended by the coastal state. Several other fixes were made to the coastline to ensure that the coastline could be used as an appropriate normal baseline for the drawing of the multiple Maritime Boundaries areas. This product will be called ‘World Countries 2014’ in this methodology page.
Following the UNCLOS distinction between Islands and Rocks – PART VIII REGIME OF ISLANDS - coastlines were created with the appropriate features for the drawing of EEZ, and another one for the drawing of TS, and CZ. Specific cases where coastal features were not contemplated for the drawing of EEZ include, among others, the Rockall rock off the west coast of Scotland and the Alijos rocks off Baja California.
Treaties and Joint Regimes
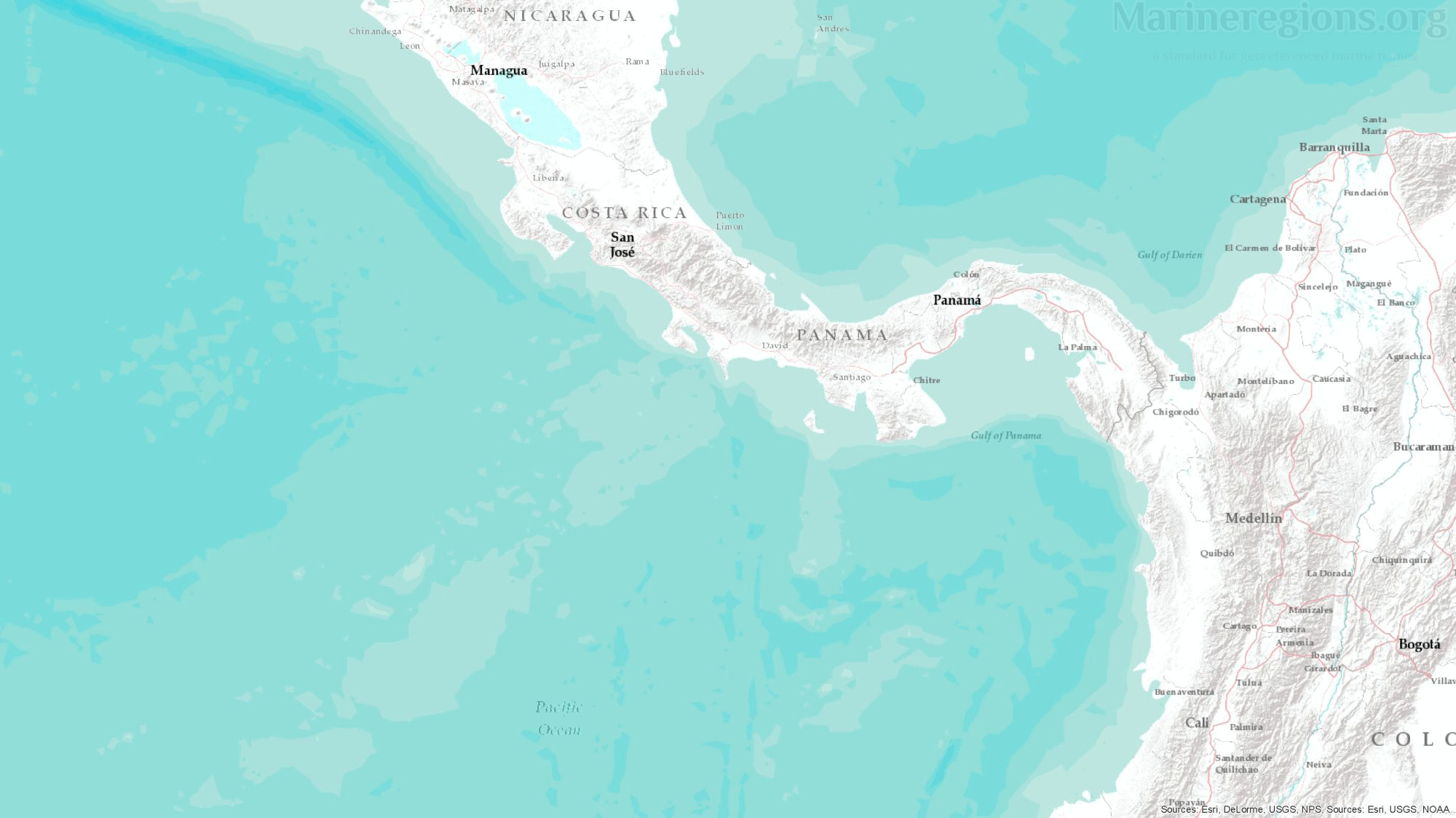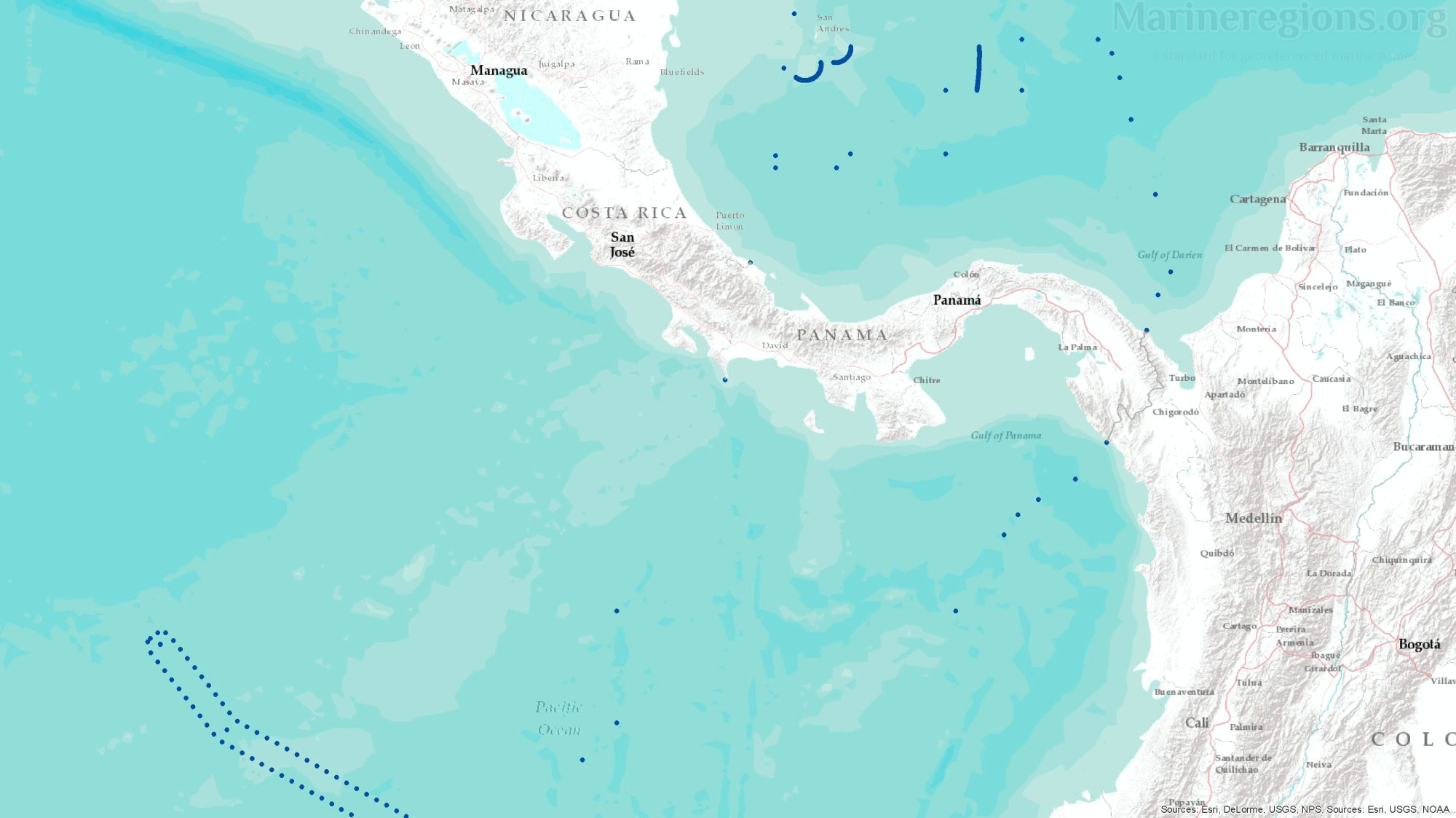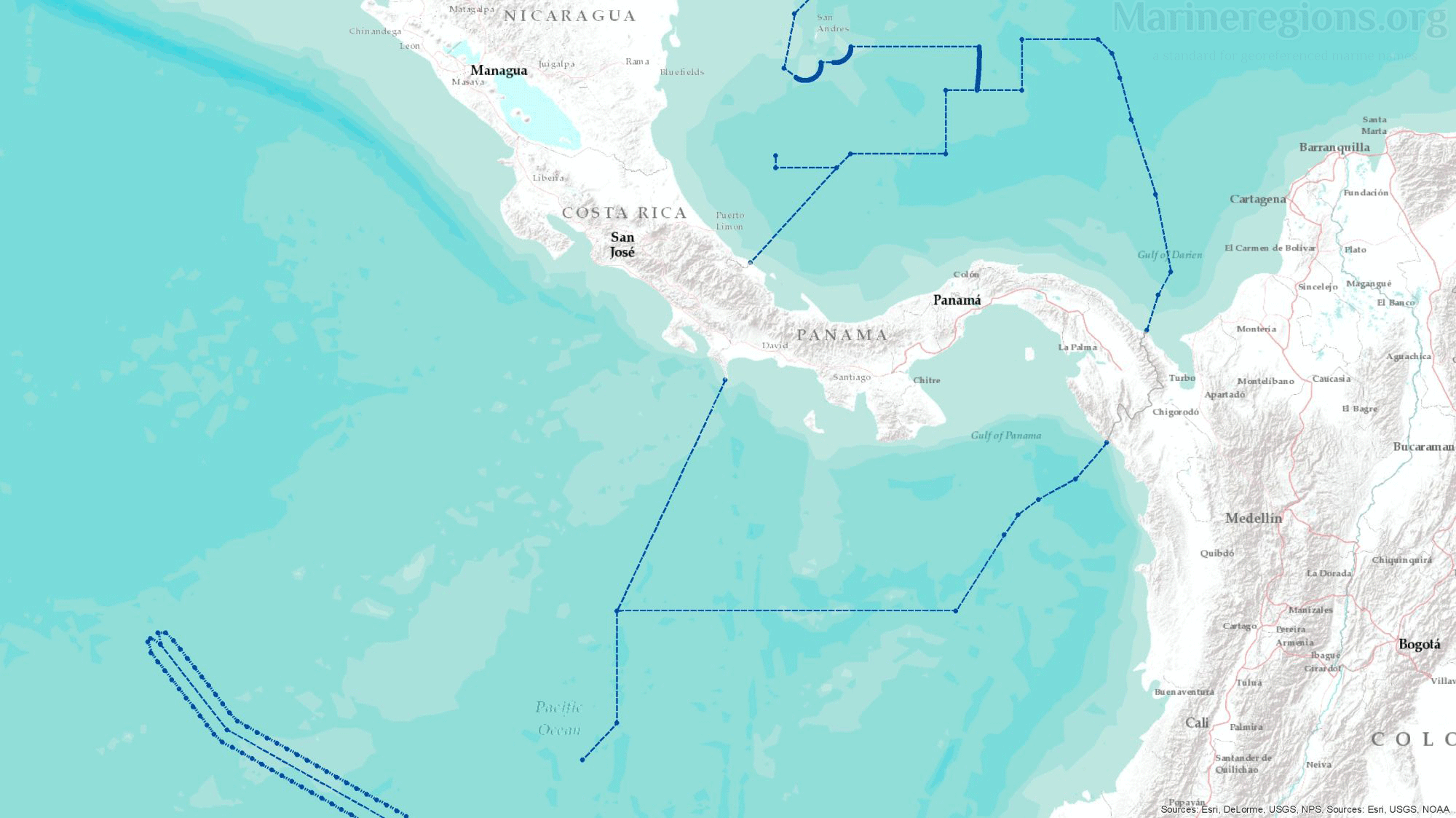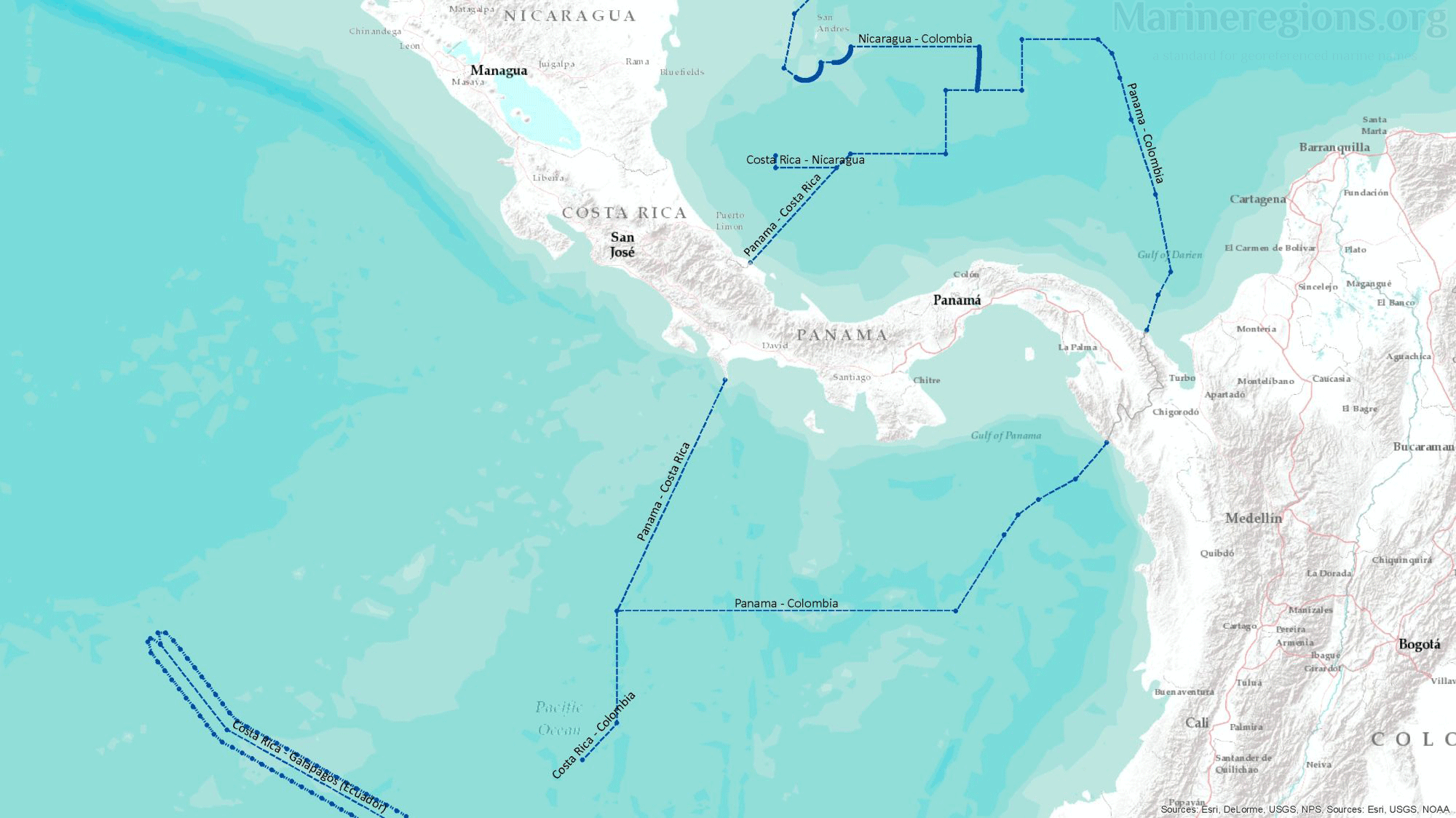
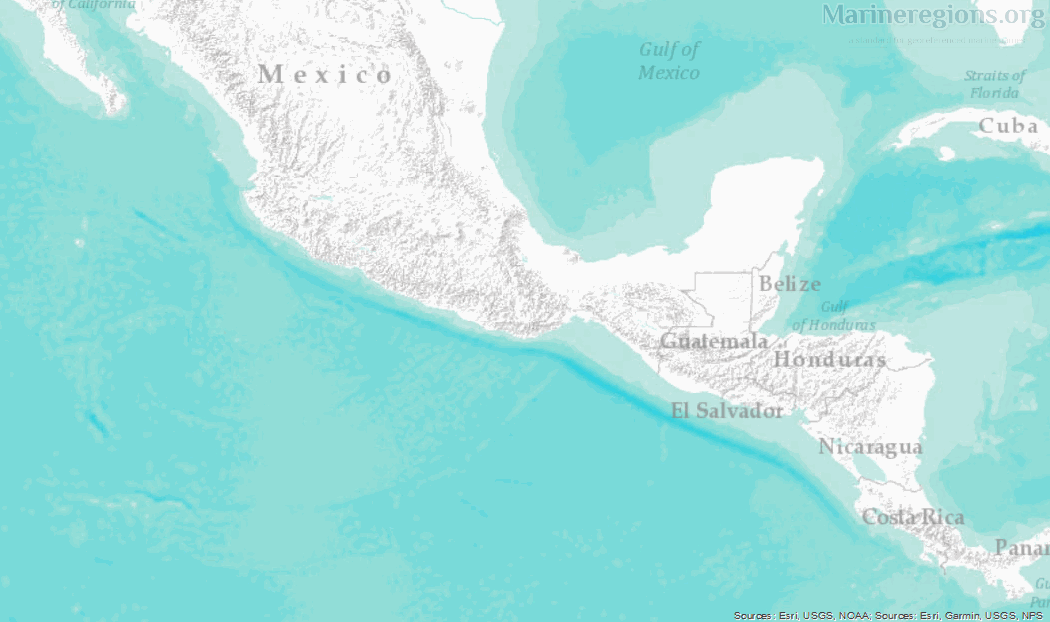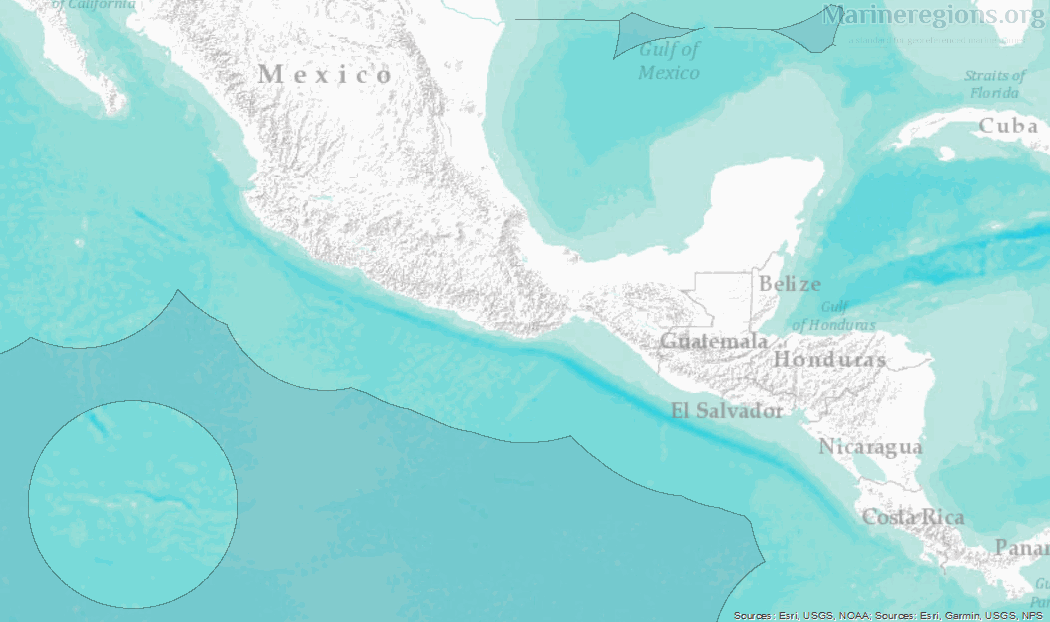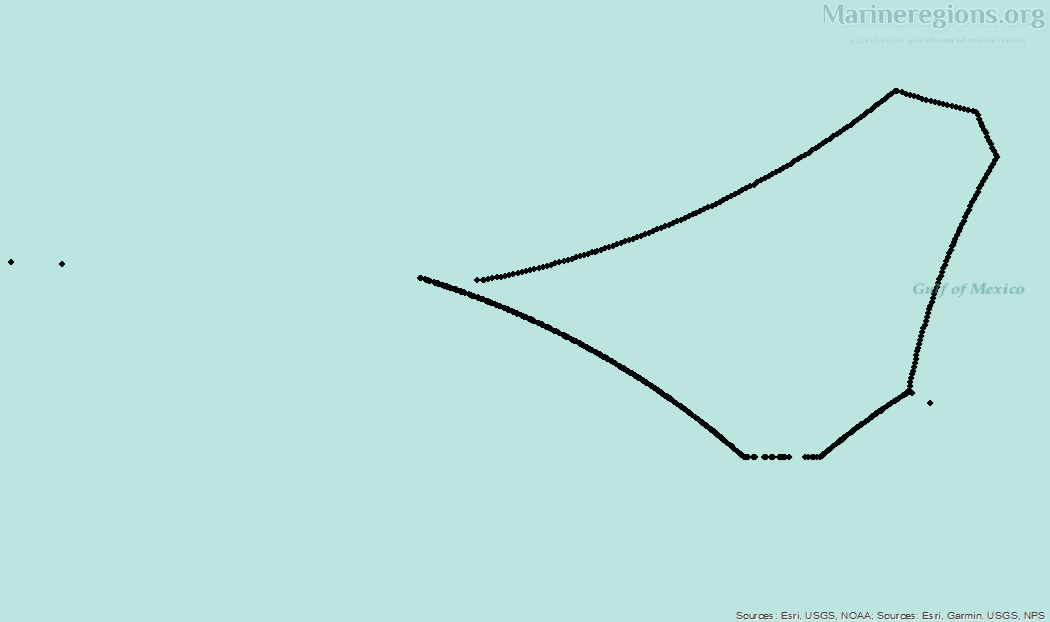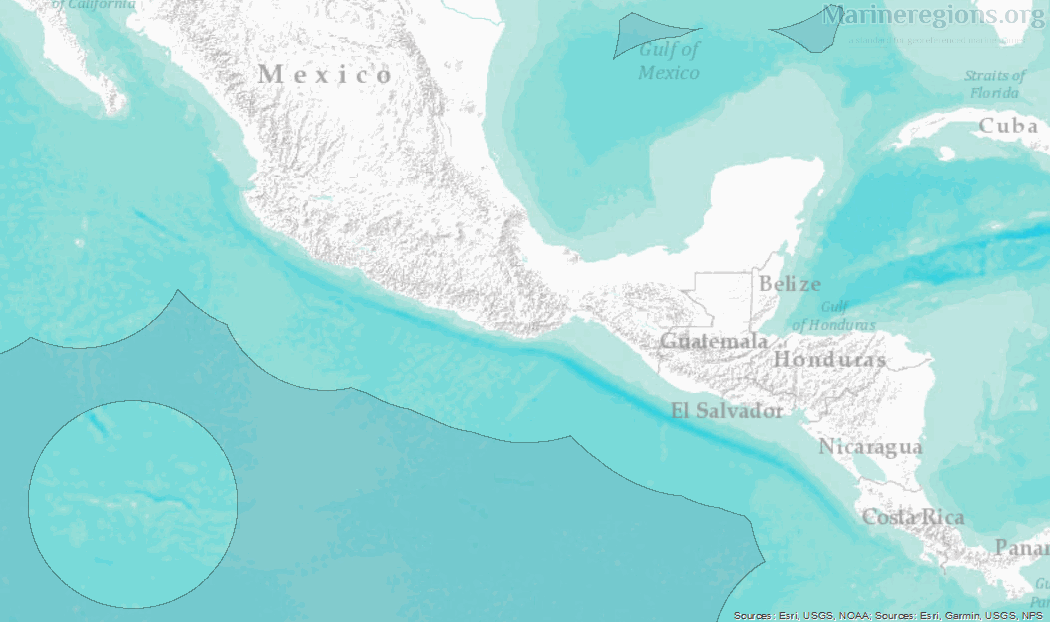
Most treaties and agreements between coastal states are submitted to the UN and gathered under the DOALOS. Points pertaining the relevant treaties were stored, converted to lines, and then added to the collection of baselines and median lines.
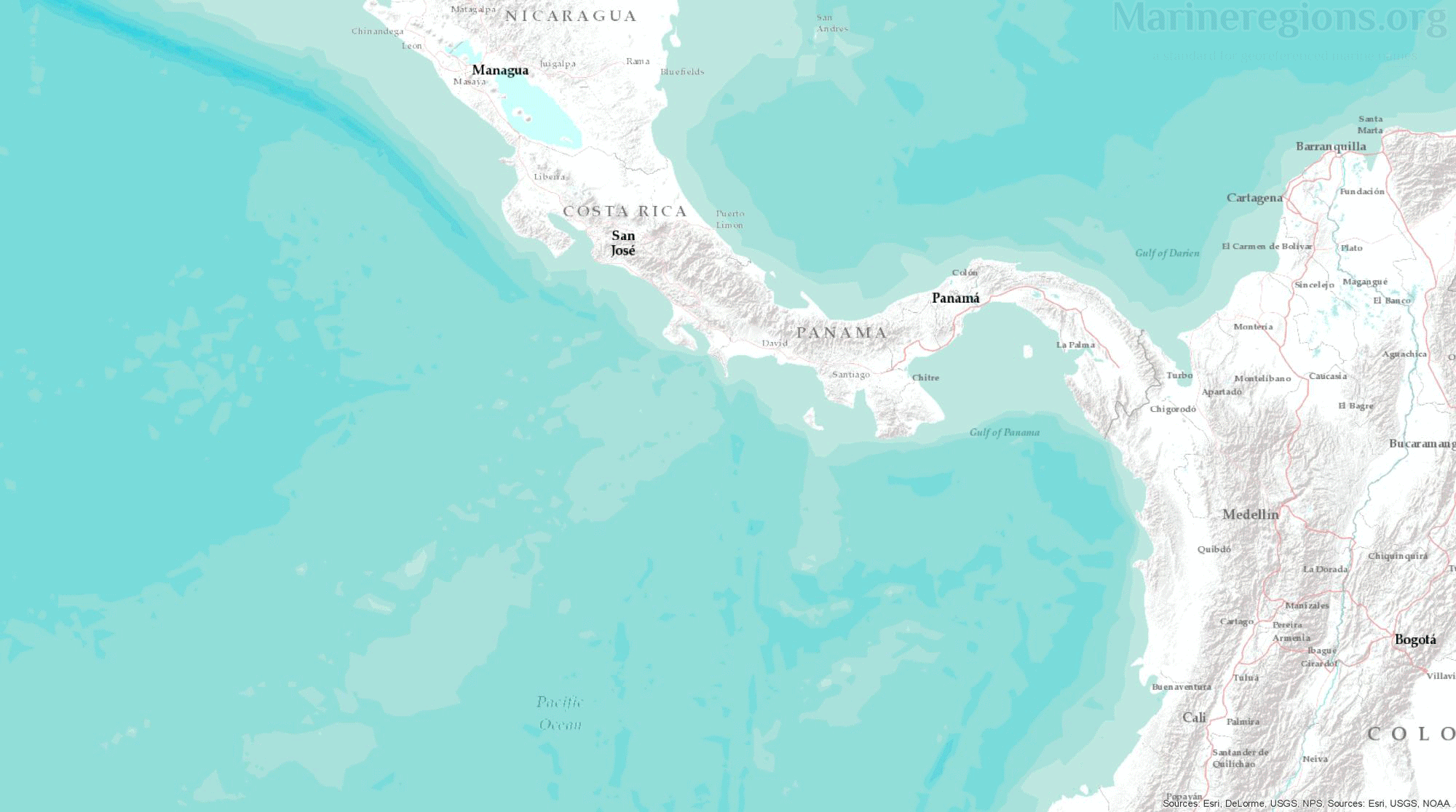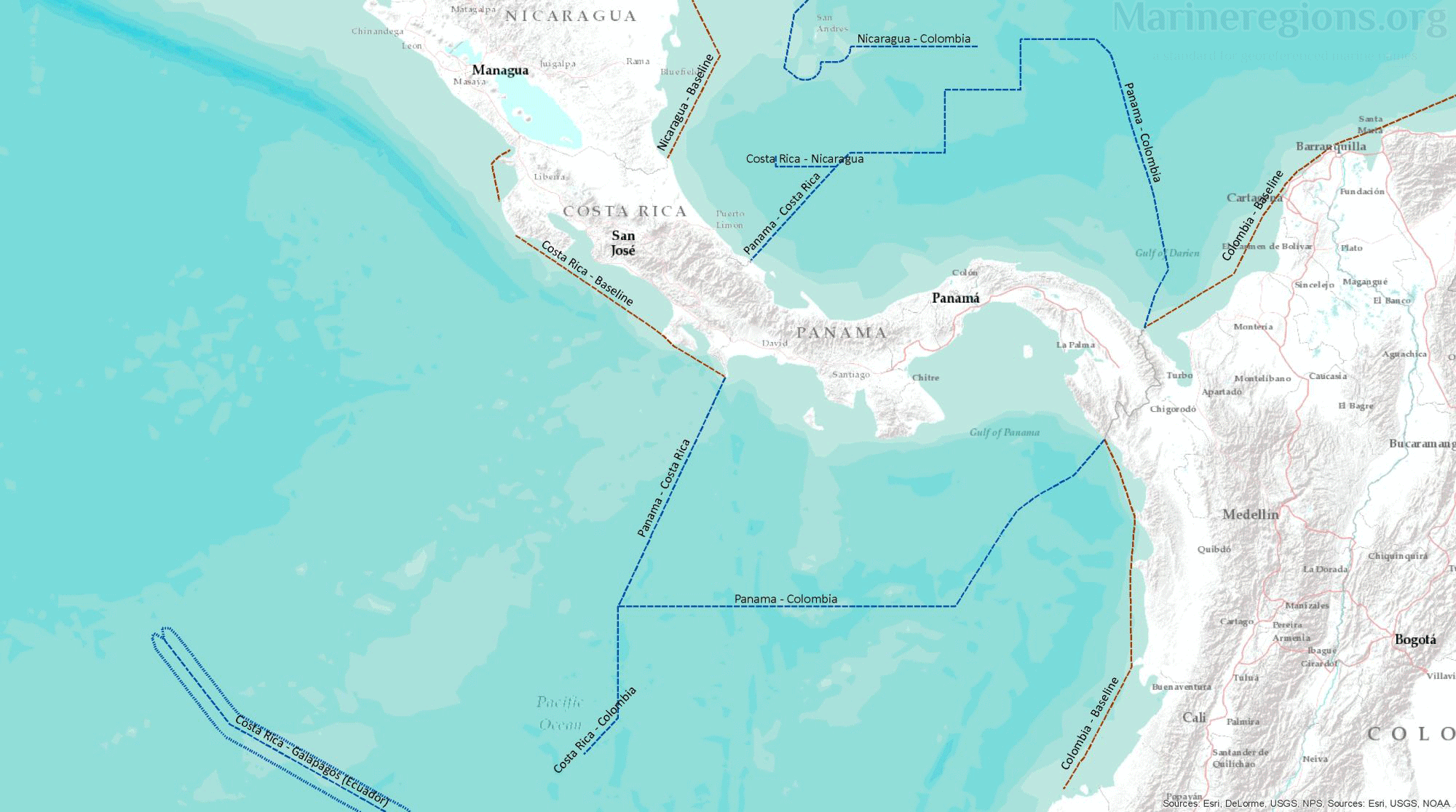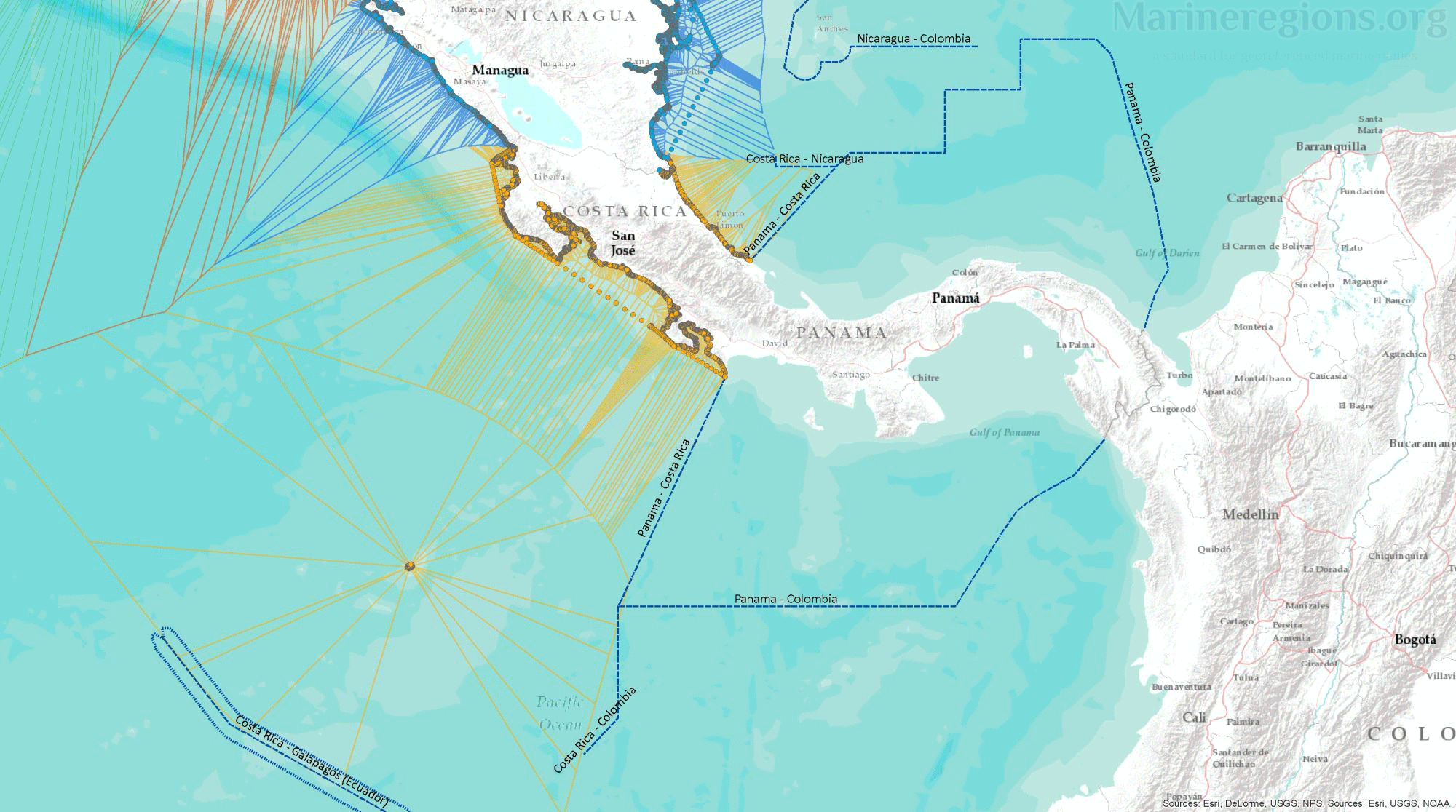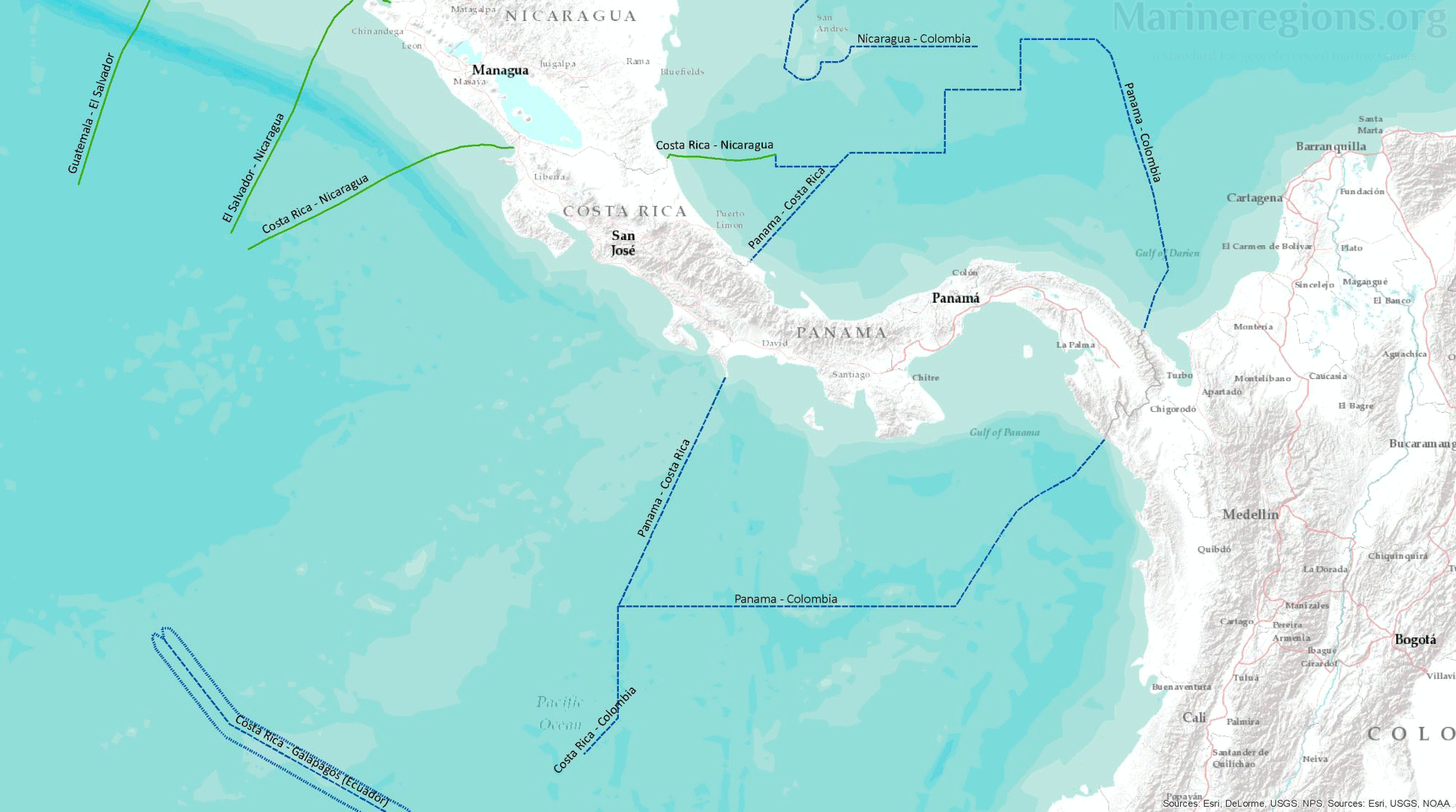
Median Lines
Unless borders at sea were defined by a treaty or agreement between coastal states, the boundary between nations was calculated by Marine Regions and defined as the Median Line – or the line connecting points which are located at equal distance from both coastal states. This was achieved by drawing Thiessen polygons rooted on points along both the straight and normal baselines.
The millions of Thiessen polygons generated are then merged and dissolved by attribute, in this case the Country name, exposing the median lines between countries.
In order to obtain regularly spaced points along the coast, both baselines were densified so that the maximum distance between points was reduced to 0.01 Degrees.
While the distance between points mentioned above was sufficient to grant equal weight to both coasts involved, this was not the case for international border estuaries and rivers, or in cases where the distance between coastal states was smaller than the maximum distance between points along the baselines. In these cases, the baselines were further densified.
Connection lines
There is an unavoidable mismatch between the median lines calculated by Marine Regions and those published by or retrieved from points from third parties. Of course, polygons cannot be drawn without an uninterrupted set of lines. Connection lines are lines added to bridge the gaps between, for instance, a median line to a treaty line. Connection lines were drawn by extending an existing line using the same angle or linking a line to the nearest relevant vertex.
Polygons
Having calculated or stored the lines defining the coast and the maritime borders between adjacent or opposite coastal states, the remaining boundary left to be calculated is the seaward outermost boundary of 12, 24 and 200 nautical miles, representing the hypothetical outer limit of the territorial seas, contiguous zones and EEZs respectively. These areas were calculated by a buffer distance measured from the combination of straight and normal baselines.
The geodetic surface area of all polygons were calculated in PostGIS and rounded to square kilometers. For version 12, we made a considerable effort to make all the geometries topologically correct. Moreover, all 0 to 360° products (centered on the Pacific Ocean) have been provided. A low resolution version of the EEZs was created with Mapshaper using the Visvalingam simplification and a 10% point retention.
Union of world country boundaries and Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs)
This dataset contains the combination of both land and maritime boundaries. It was developed by merging the World Countries 2014 dataset as a proxy for country boundaries with the Exclusive Economic Zones. This operation was performed in ESRI ArcGIS Pro 2.5.0 using the Pairwise Dissolve tool. The dissolved field was the "MRGID_EEZ". Landlocked countries and joint regimes were separated prior merging and added back afterwards.
The resulting polygons had several gaps due to small differences between the coastlines of the EEZ and the World Countries 2014 datasets. These were filled using the Delete Holes tool from QGIS 3.10 setting a minimum area threshold of 0.1. Unfortunately, in this step also enclaves and semi-enclaves were considered holes and thus deleted from the territory of the surrounding state. The enclaves and semi-enclaves with their EEZ were extracted and overlaid with the product by using the Difference tool from QGIS 3.10.
High Seas
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea describes the high seas as ‘all parts of the sea that are not included in the exclusive economic zone, in the territorial sea or in the internal waters of a State, or in the archipelagic waters of an archipelagic State.’
The High Seas product was created by subtracting the Union of the world country boundaries and Exclusive Economic Zones (see above) from a world bounding box (-180, -90, 180, 90) in PostGIS using the ST_Difference function. The polygons in Union of world country boundaries and Exclusive Economic Zones were previously combined in a single geometry using the ST_Union function. Afterwards, resulting spikes and slivers were deleted manually from the dataset.
Extended Continental Shelves
The Extended Continental Shelves represent the portion of the continental shelf that extends beyond 200 Nautical Miles, as submitted by a State to or recommended by the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS), or deposited with the Division for Ocean Affairs and the Law of the Sea (DOALOS), or claimed by (a) a Non-Party State to UNCLOS or (b) a Party State to UNCLOS through mechanisms other than a submission to the CLCS or a deposit to DOALOS.
Points from these official documents were digitized and then converted into lines. These lines were subsequently transformed into geodesic lines using the Geodetic Densifier tool in the QGIS Shapes plugin, by adding additional vertices along geodesic paths within the shape for every nautical mile.
Where these lines did not intersect with their inner boundaries (i.e. the outer boundaries of the Exclusive Economic Zones), geodesic connection lines were created, either linking the line to the closest point on the outer EEZ border, or to the edge of the EEZ. By combining the lines, connection lines, outer EEZ boundaries, relevant treaties and world outline, the resulting polygon dataset was created using the Feature to Polygon function in ArcGIS.
Map interface
It is possible to download the used treaties in PDF and the coordinates of the boundaries in GML (Geography MarkUp Language). The geodatabase is not only consultable through a web form, but also through a map interface where one can zoom, pan or query the GIS layers. Linking makes it simple to jump from the information pages to the map interface and back. The latter was implemented using the open-source GeoServer, which supports Open GIS standards. This allows making the GIS layers available through WMS (Web Map Services) and WFS (Web Feature Services).
In order to optimize the dissemination of the global maritime boundaries database, a KML or or Keyhole Markup Language file has been created. KML is the filetype that can be viewed in Google Earth or on Google Maps. The KML file is actually a link to the web services in GeoServer that can be opened in Google Earth or Google Maps.
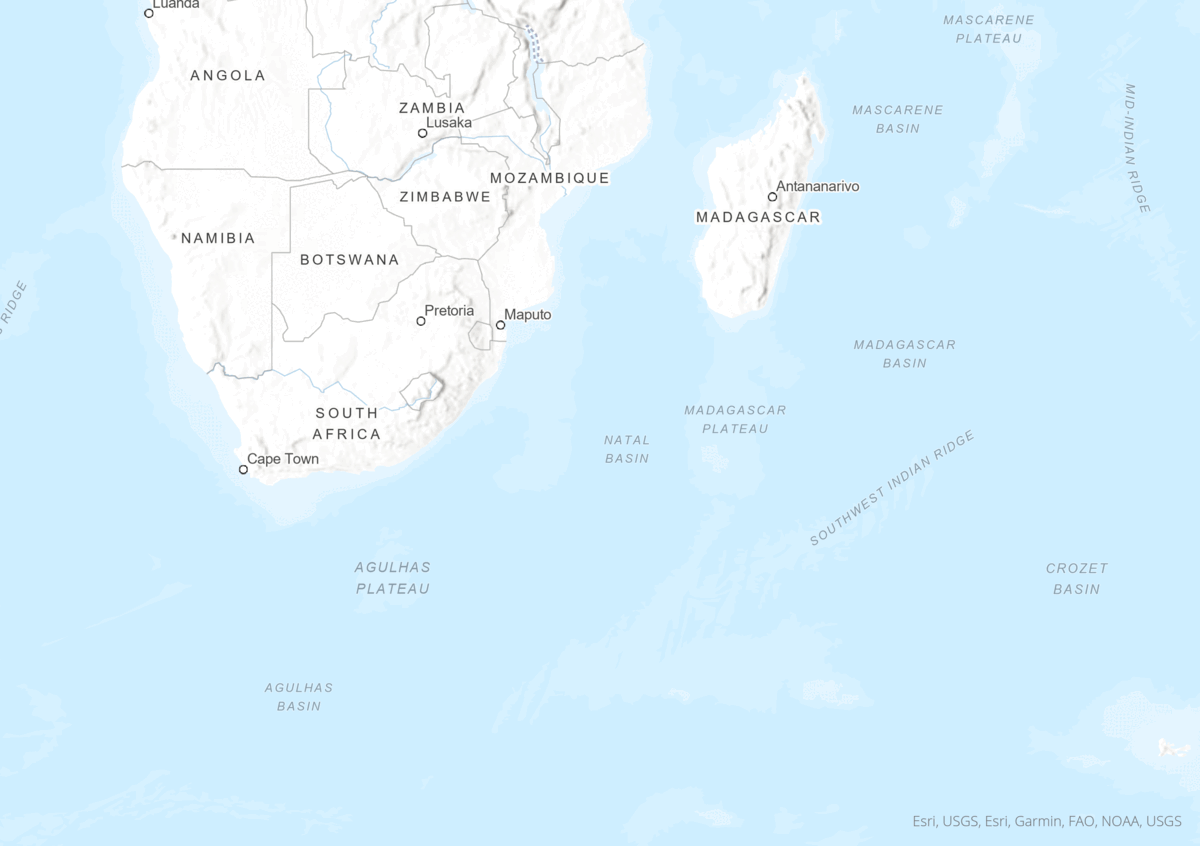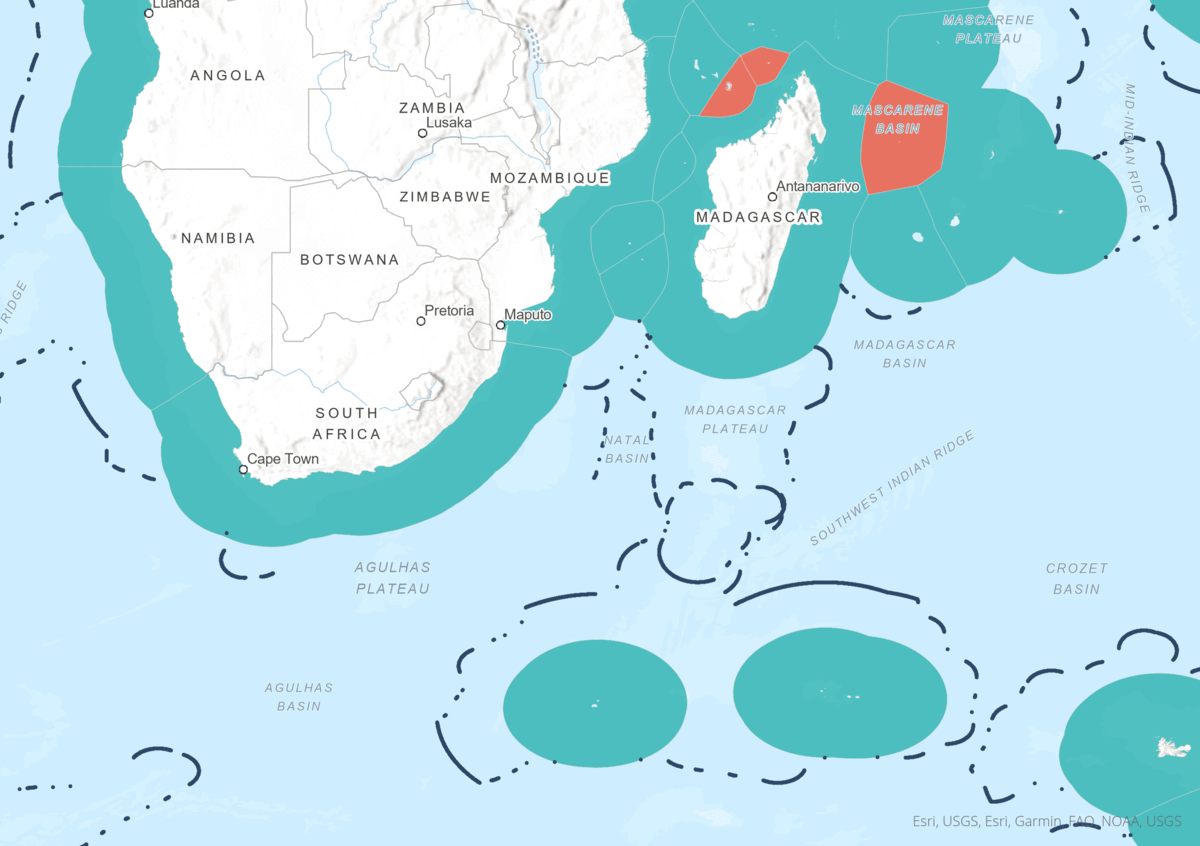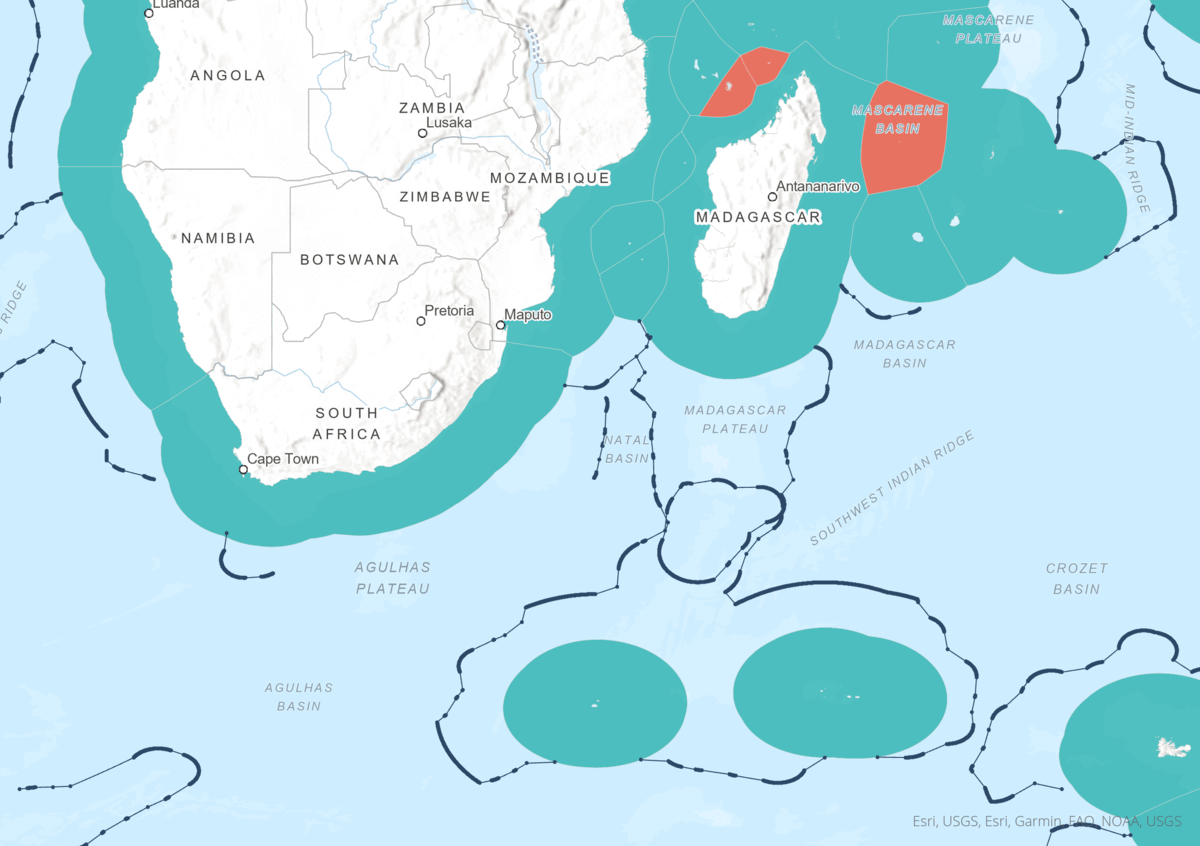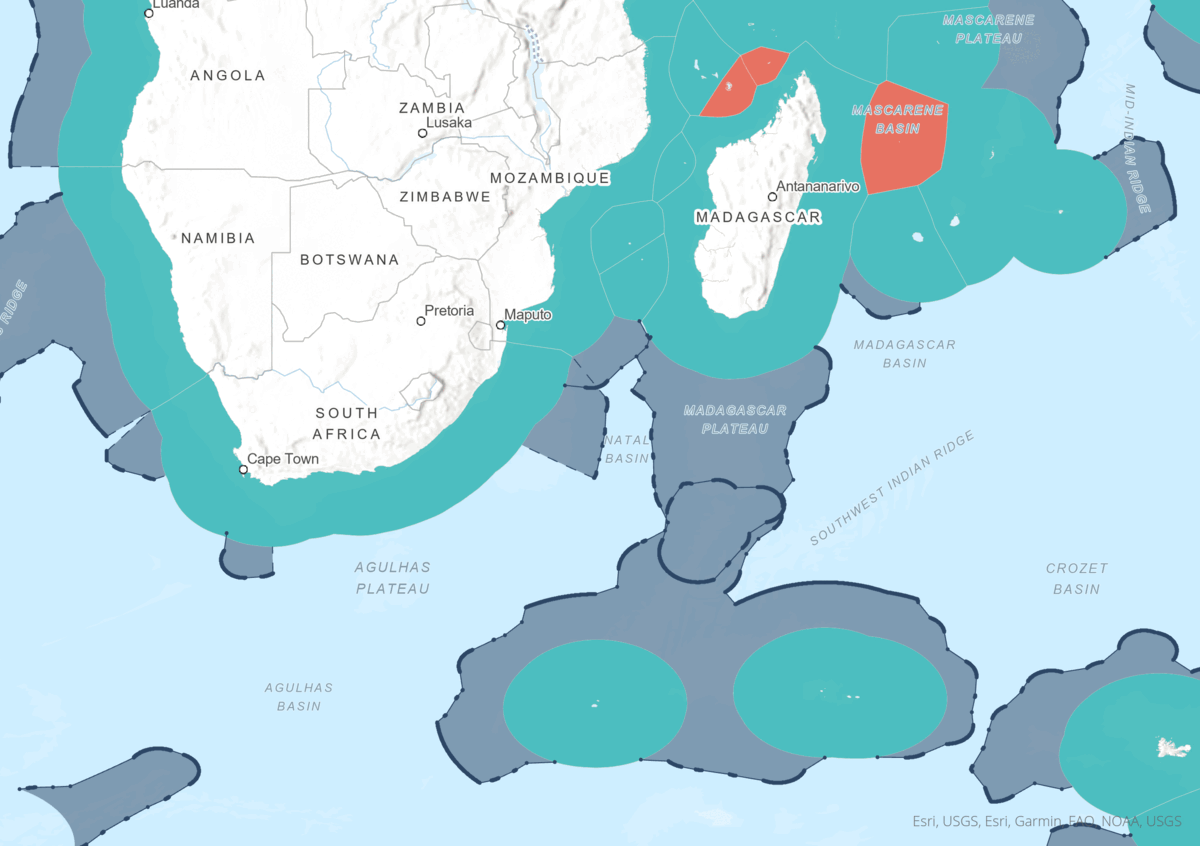
Animation illustrating the drafting of the Maritime Borders from start to finish.
Check also the Frequently Asked Questions.